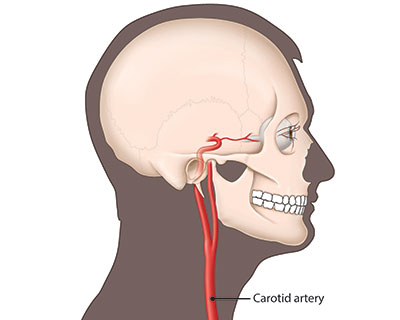
A buildup of cholesterol in the arteries causes a plaque to form. This buildup eventually narrows or hardens the arteries. Pieces of plaque can break off into the blood stream, slowing or blocking blood flow to the eyes and brain.
Vision problems may be warning signs of carotid artery disease. One may notice that one side of the body is weak or numb, and or may lose vision on the same side of body.
Know the warning signs of a possible blocked carotid artery. If you have these symptoms, call your doctor right away.
- Vision that seems like a mild shadow is being drawn over the eye. This could be due to a temporary blockage in your carotid artery, called a TIA (transient ischemic attack, or “mini-stroke”). It may last a few minutes to an hour. This could be a warning sign that one may soon have a blocked carotid artery.
- Loss of side vision or total vision loss. This, along with muscle weakness or paralysis on one side of the body, may be a stroke. This can happen when the carotid artery is completely blocked. Do not wait—get help right away. Call 911
People at increased risk for carotid artery disease are those who:
- smoke
- have high cholesterol
- drink a lot of alcohol
- are obese
- have high blood pressure
- are not physically active enough
- have a family history of carotid artery disease
Except for family history, one has some control over these risk factors. Talk with your doctor about ways to help reduce risk of carotid artery disease. Your doctor may suggest a healthy diet, stay at a good weight, be active each day, and possibly take medicine.
Diagnosis of carotid artery disease
Tests may include certain types of scans of the body. Those scans can show how well blood is flowing through your carotid arteries. An Eye exam with photography and OCT would be helpful.
Treatment of carotid artery disease
A team of doctors is necessaryto treat carotid artery disease. Treatment may include:
- blood-thinning medications (such as aspirin) to help prevent blood clots
- medicine to lower blood pressure
- surgery to remove a blocked section of the carotid artery







